According to research, enterprises experience 130 security breaches per year, per organization, on average, which costs anywhere from $120,000 to $1.24 million. These damaging attacks launched by cyber criminals can seriously impair an eCommerce store’s ability to operate.
While many eCommerce sites invest in fantastic UX and UI, they frequently overlook cybersecurity. And yet brute force attacks and fraudulent scams committed by cyber criminals incur significant financial costs, with repercussions that can permanently damage a company’s reputation and customer loyalty.
However, there are ways to safeguard your business—like following the guidelines below! Read on to learn about the different types of cyberattacks, and how you can protect your online store from these serious security breaches.
Why Is Ecommerce Security Important?

Without proper security, you put your brand and your customers at risk of suffering fraud or identity theft. A survey by PricewaterhouseCoopers concluded cyber crime is now the biggest threat to eCommerce as hackers and organized crime groups become increasingly sophisticated.
Therefore, cybersecurity is essential to protect against a loss of revenue and business credibility. Even small stores catering to niche markets are at risk if there are gaps in their online security. Statistics show that 20% of small eCommerce businesses fall victim to fraudsters and of that 20%, 60% end up closing due to fraud victimization.
Customers who feel safe buying from you will continue to return to your store, even if your competitors offer the same products or services at a reduced price. Consumers value security more than saving a few dollars, hence the paramount importance of having security protocols and measures in place to keep threats at bay.
Below are some essential steps you can take to secure your eCommerce store.
10 Security Measures to Make Your Ecommerce Website Safe
Identifying where opportunities exist for hackers to carry out attacks and following the correct protocols to prevent them from doing so will make your customers happy and safe when shopping online.
Step 1. Choose a Secure Hosting Provider and/or Ecommerce Platform
As a rule of thumb, we recommend using credible eCommerce platforms like Shopify, Magento, WooCommerce, BigCommerce, etc. Most already have basic security measures in place and ample plugins to bolster data safety.
Regardless of which platform you use, ensure it has baked-in security measures and maintains PCI compliance (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard). Moreover, make sure you’re running the latest version of the software. Whenever there’s a new patch available, install it immediately.
Some eCommerce platforms are self-hosted, meaning store owners are responsible for hosting and storing data. If this applies to your online store, then you’ll want to choose a secure hosting provider.
Uptime, security patches, traffic handling capacity, and storage are important considerations, as well as how frequently your hosting provider backs up your online store. A good provider should be accessible 24/7 and have 99.9% uptime.
Step 2. Get an SSL Certificate

Reputable eCommerce platforms place great emphasis on security and come with or have SSL certificate integrations. An SSL certificate is technically a piece of code on your web server that provides security for online communications.
Websites that start with “HTTP” do not have an SSL certificate and are not as secure as those that begin with “HTTPS.” SSL certificates contain a website’s public key (data encryption) and a website’s identity, along with related information.
Your online business needs an SSL certificate to keep consumer data secure, verify website ownership, prevent hackers from creating a fake version of your store, and secure user trust. Moreover, Google announced in 2014 that HTTPS is a light ranking factor and in 2017 the search engine began red flagging sites still on HTTP with “not secure” warnings.
Therefore, an SSL is necessary to instill confidence in consumers and search engines.
Step 3. Protect Your Customers’ Data
Building trust is an essential aspect of healthy customer relationships. One of the easiest ways to do so, besides offering high-quality products and services, is to protect your customer’s data.
Be Transparent
Facebook’s data breach scandal made consumers wary of sharing data with social media platforms and eCommerce stores. Naturally, your online store must be compliant with data laws. Additionally, you should be transparent with customers about how their data is being collected, used, and protected, as well as provide options for them to opt out of data collection.
Encrypt User Data
Payment providers like Visa and MasterCard require retailers to encrypt card details by default during transaction processes. However, it’s dangerous to store this data on company servers as there is a much higher risk of financial fraud. And it’s not just payment cards that should be encrypted—the theft of any personal customer data from your servers will have a much lower impact if it’s encrypted by a secure third party.
Verify but Don’t Store Data
To expand on the previous point; it’s important to distinguish between collecting data you need like names and email addresses and data you don’t need such as credit card details. eCommerce businesses don’t really have compelling reasons to store this data, especially when it’s a liability. Thus, creating a framework that allows third-party processors to handle credit card data is a much safer bet.
Step 4. Implement Two-Factor Authentication
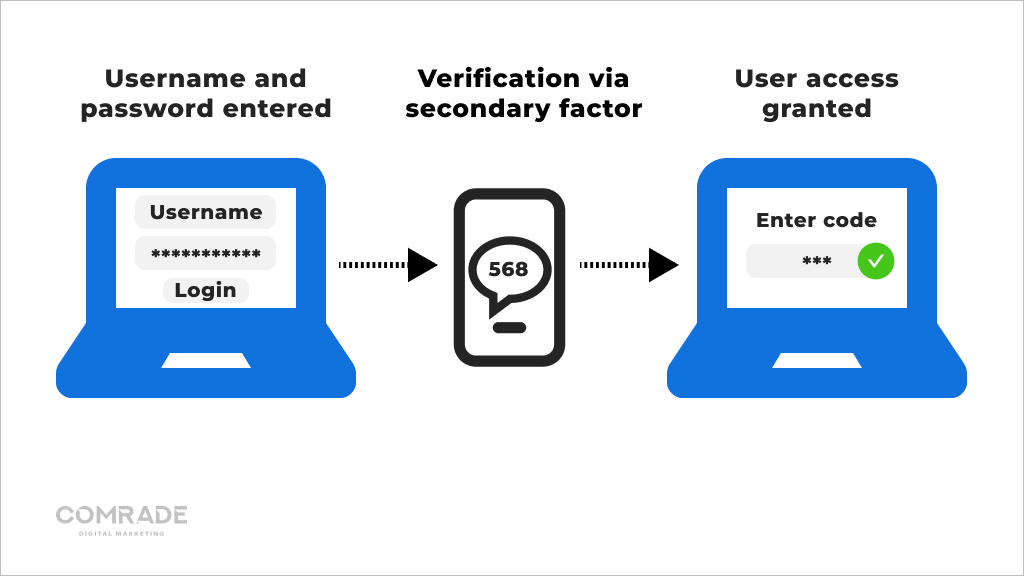
Every so often, an eCommerce store’s weakest link is its customers. Weak or repeated passwords are more prone to security breaches by bots or hackers. When it comes to login credentials, ensure customers use complex passwords that feature upper and lowercase letters mixed with numbers and symbols. For an extra layer of protection, turn on two-step authentication (2FA).
This security process requires users to provide two means of identification; one is typically a username/password combo, while the second is an auto-generated code sent to the user’s verified phone number. Hackers might crack a user’s password, but they can’t steal this code, which usually expires after a short duration.
Step 5. Secure Your Admin Panel and Server
In the same way that customers should use complex passwords, so too should you and your employees. Always create passwords that are difficult to figure out and make it a habit of changing them frequently.
It’s also a good idea to restrict user access to admin panels and define user roles. Each user on your team should only perform their specific roles on the admin panel. This streamlines processes and makes it easier to detect cyberattacks if they occur. Furthermore, you can configure your panel to send notifications whenever a foreign IP tries to access it.
Most eCommerce companies have set protocols and security measures in place that employees are required to follow. Some even have data security managers to uphold eCommerce security.
Step 6. Use WAF to Avoid Hacking
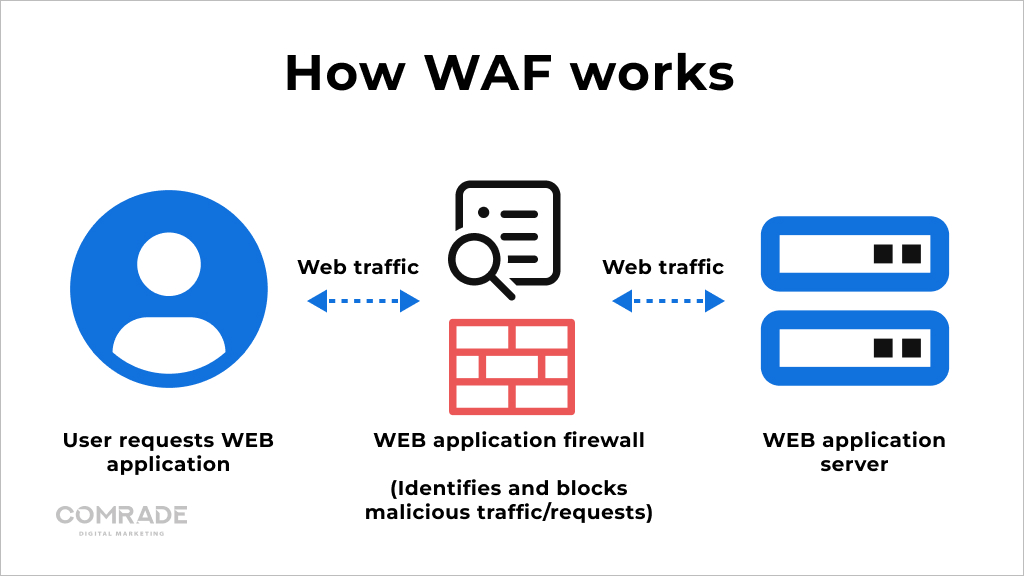
A web application firewall (WAF) is an application firewall that monitors, filters, and blocks harmful traffic before it reaches a web server. It prevents the exploitation of potential weak spots in your eCommerce security, such as the wrong system configuration, file inclusion, SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and more.
WAFs are different from traditional firewalls because they do more than just block specific IP addresses or ports—they actually look for signs of cyber threats or possible injection. They analyze the headers and contents of a request and ask for proof that a human has launched a request and not a bot.
A good WAF will immediately block fraudulent traffic or conduct further tests to prevent harmful programs from proceeding. A Web Application Firewall is typically configured according to two security models:
- Whitelisting model: The WAF only allows approved traffic to access your eCommerce website.
- Blacklisting model: The WAF is configured to block specific vulnerabilities, malicious actors, and attack signals. For example, you can instruct the firewall to block IP addresses arbitrarily sending large amounts of high traffic.
It’s also possible to apply a hybrid model and modify your WAF according to your website security’s risk profile and requirements.
Step 7. Set Up a Strong Payment Security System
Your payment system is one of the most critical parts of your eCommerce website. It’s the place where you and your customer’s money are at stake if you don’t guarantee a secure electronic transaction.
Choosing secure payment gateways should be done with the utmost care to guarantee compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS).
A reputable payment gateway provides support and maintains PCI compliance. Some payment processors even reimburse money lost due to fraud that occurs through security breaches. When adding commerce security measures to payment gateways, you should provide customers with additional options that optimize conversion rates but safeguard your company.
For instance, some gateways request a customer’s Card Verification Value (CVV) to validate card-not-present transactions either on the phone or online. A hacker won’t be able to use a stolen credit card number as this information is only available if they can reference the actual card.
Step 8. Utilize Strong Anti-malware Software
Malware is malicious software used by hackers to query submission forms and access your eCommerce website’s backend to collect customer data without any trace. You can prevent this by installing antivirus software that regularly scans your entire system to ensure the complete safety of your eCommerce site.
Anti-malware software uses complicated procedures to flag nefarious transactions in time for you to act. Timely detection and blocking of phishing attacks and fraudulent sites are a must for website security. Some antivirus products even offer protection of mail and file servers in addition to individual computer protection.
There’s a lot of subpar anti-malware software out there, so when choosing yours be certain it includes:
- Reactive file scanning that vets new files for danger before you open them.
- Complete system scans that ensure no malicious software lurks undetected.
- Web browsing protection that assesses URL links to assess their safety and potential risks.
Step 9. Backup Your Data
80% of small and midsize online businesses have experienced downtime equating to financial losses from $82,000 to $256,000 for a single event! Data loss is incredibly common in the eCommerce industry. Whether it stems from human error or a malicious software attack, it’s something you want to avoid at all costs.
Every department of your eCommerce business needs data to function—from marketing communications to fulfillment. Think of all the files, folders, product descriptions, and payment data that should be backed up.
In the case of third-party vendors, most only back up their platforms, so if there’s an error on your end, you might never be able to recover your data if you don’t perform backups. A data breach results in lost revenue, customers, and credibility.
It’s simply not worth losing months or years of work due to security negligence. Always ensure you have several file backups of valuable data, including your entire eCommerce website. In a worst-case scenario, you won’t have to worry about your valuable data being held hostage by hackers because you’ll have multiple copies.
Step 10. Educate Your Staff on Cyberattacks
Your employees should be aware of laws and policies pertaining to the protection of user information (both your company’s and your customers’). For example, they shouldn’t share login credentials, and personnel who have access to sensitive customer information should be vetted and then trained in security protocols.
Continually emphasize the critical nature of security and the responsibility everybody has to protect company data because it affects your business’s integrity. When and if necessary, you might also want to educate your clients or customers.
Additionally, once an employee tenders their resignation, you should expunge their details and revoke all employee access to prevent them from committing cyber crimes against your business, or accidentally having their employee authorization details fall into the wrong hands.
Common Ecommerce Security Threats
Examples of security threats include misuse of personal data, monetary theft, phishing attacks, hacking, and fraudulent credit card transactions. Let’s take a look at the most common ones and how to spot them.
Malware and Viruses
Hackers and online criminal syndicates inject harmful programs (viruses) into eCommerce websites without their knowledge or consent with the primary goal of stealing private data. Generally, there are two objectives of such attacks:
- Ransomware—blocking the performance of your online business until the criminals responsible receive a ransom payment.
- Viruses—infecting and dispersing harmful files with the aim of damaging, corrupting, and destroying business and customer data.
Viruses can be difficult to detect although slow website performance, missing files, constant pop-ups, and disabled security software are all potential signs of a security breach.
Spam
Spammers target eCommerce websites because there are just so many out there that allow account creation, providing an easy opportunity for getting backlinks or hacking. Spambots, for example, sign up for emailing lists with fake and real addresses and then damage your eCommerce site’s reputation by bombarding your email subscribers with spam mail.
If you experience a sharp decrease in unsubscribes, dips in open rates, or spam complaints, your business may be a victim of spam. To prevent spammers from creating fake accounts on your eCommerce site, you can install Recaptcha by Google.
To quote the search engine: “A “CAPTCHA” is a Turing test to tell humans and bots apart. It is easy for humans to solve, but hard for “bots” and other malicious software to figure out.”
Phishing
Phishing manipulates employees into performing actions that benefit cyber criminals. It’s often used to steal user data such as login credentials and credit card details.
Usually, the hacker will parade as a trusted entity and dupe the victim into opening an email, instant message, or text message with a malicious link that installs malware as part of a ransomware attack or to steal sensitive information.
A variety of different phishing attacks can threaten an eCommerce website’s security:
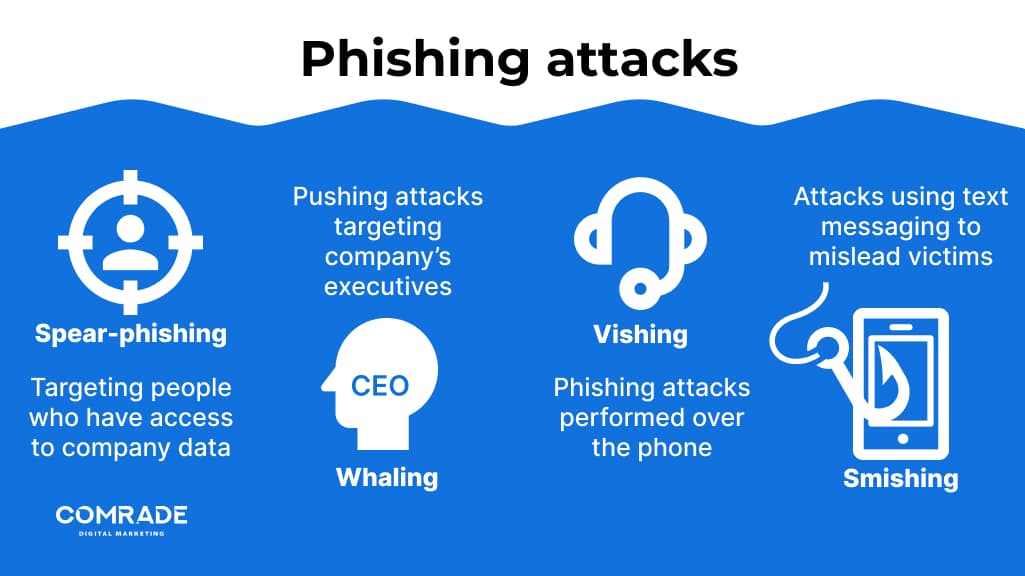
- Spear-phishing—targets those in your company who have access to sensitive information, such as system administrators, executives, and those working in the accounts department.
- Whaling—targets C-level executives by using extreme tactics to encourage the executive to click on an infected attachment. For instance, the hacker may threaten to sue your company if you don’t open a specific email.
- Vishing – a form of phishing where criminals use mobile phones to extract information or manipulate their victims into carrying out behavior that results in stolen data.
- Smishing – Similar to the above tactic, smishing uses mobile messaging channels like WhatsApp and SMS text to manipulate targets.
More than 300,000 phishing attacks were recorded last year alone. Currently, there is also an ongoing trend of phishing attacks levied at cryptocurrency companies. Needless to say, it’s safe to assume most online businesses will come across such scams at some point.
The best way to avoid falling prey to phishing is to implement eCommerce security best practices like using email and content filtering, as well as educating employees with security awareness training.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are malicious attempts to make an online service unavailable to users, usually by temporarily disrupting or suspending the host server’s services.
DDoS attacks send multiple malicious requests with the aim of exceeding a website’s capacity to handle the volume of requests, preventing an eCommerce store from functioning correctly.
If you experience a DDoS attack, your store will suffer in one of the following ways:
- Its response to requests will be far slower than usual.
- Some—or all users’ requests will be completely ignored.
Some attacks are carried out by individuals wanting to make a political statement or exploit security vulnerabilities, or express disapproval. Others are financially motivated, such as disrupting or shutting down a competitor to steal its business or demand a ransom.
The best way to handle these security threats is to have a proper commerce security plan and use a content delivery network (CDN). A CDN balances website traffic across servers in different locations, making it difficult for hackers to spot and attack your original server.
Trojans
A Trojan Horse Virus is a type of malware that’s disguised as a legitimate app or software program. Usually, hackers perform social engineering to hide malicious code within legitimate software to gain access to valuable data.
Computers and mobile devices infected by Trojan malware can spread it to other devices. Hackers will turn the original device into a zombie computer, meaning they will gain remote control of it without the user knowing, so they can continue sharing malware across a network of devices (a botnet).
The user who spreads the malware won’t know anything bad has happened, as their computer or device may continue to work normally.
However, common signs of a Trojan infection include:
- Strange device behavior—programs start running without you having opened them.
- Pop-up and spam interruptions—an increase in browser pop-ups and spam.
- Poor device performance—slow operating or inexplicable software crashes.
Running regular security updates and only downloading attachments and programs from trusted sources can reduce the probability of Trojan attacks.
Financial Fraud and Faulty Transactions
Financial fraud refers to any false, illegal, or illegitimate commercial transaction conducted through the internet. Typically, the fraudster will impersonate a legitimate user and make purchases without valid authorization.
Card Testing
This is when hackers illegally obtain credit card numbers and make eCommerce purchases to test their validity and spending limits. By the time merchants realize they’ve been part of card testing fraud, the criminal would have likely already made several large purchases.
Account Takeover
Account takeover is a form of identity theft that occurs when criminals gain access to customer accounts and change their login details, make purchases, withdraw funds, and access other accounts owned by the users. This type of fraud is incredibly damaging to customer relationships.
Interception Fraud
With interception fraud, criminals use stolen credit cards to make online purchases and ship the products to the address that’s on file for the credit card at checkout, but then intercept the package before it’s delivered.
Chargeback Fraud
Also called friendly fraud, this is when consumers fraudulently attempt to secure a refund using your chargeback process to get items for free. They will claim they never ordered the item, or it wasn’t delivered. It’s difficult to prove, and in most cases, the issuers will provide a chargeback to keep the customer happy.
Refund Fraud
Refund fraud occurs when a bad actor purchases a product or service using a stolen credit card and then has it refunded on their credit card. A tell-tale sign is when a customer requests their refund needs to be processed on a new credit card. It’s estimated that one in five refunds is fraudulent.
Sadly, eCommerce merchants are more vulnerable than brick-and-mortar stores. Therefore, you must stay informed and implement the correct information security management systems or fraud protection solutions to protect your bottom line.
SQL Injections
SQL injections are a code injection technique that lets hackers access confidential database information such as user lists, sensitive company information, or private customer details. A successful attack may result in the deletion of data tables or allow the attacker to gain administrative rights to a database.
This type of attack is dangerous because attackers can:
- Obtain login credentials and impersonate users and abuse their privileges;
- Alter or add new data to the accessed database;
- Delete databases; and
- Use illegally obtained permissions to access other systems.
Prevention techniques like input validation, parameterized queries, and stored procedures can prevent these attacks. However, they work even better combined with a trusted WAF.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Without getting overly technical, cross-site scripting is a client-side code injection attack that works by manipulating a vulnerable website, so it returns malicious JavaScript to consumers. The web page or web application the victim visits becomes the vehicle to deliver the malicious code.
Forums, message boards and webpages that allow comments, i.e. reviews are prone to XSS attacks, which are commonly used to deface websites or change their content or even redirect users to another web page with phishing prompts or malicious content.
Because the end user’s browser has no way to know the JavaScript is untrustworthy, the malicious script can access cookies, token sessions, and other sensitive data retained by the browser and used by your website.
Keeping software up to date and sanitizing and validating input fields on both your client and server side are added precautions to protect against damaging XSS scripts.
Conclusion
Your eCommerce website is an opportunity to leave a lasting impact on your customers. Making it functional and ensuring it has top-notch eCommerce security measures can be challenging to handle on your own. For personalized assistance with your eCommerce site, turn to Comrade.
We offer robust WooCommerce web development services, Magento development, and digital marketing strategies to help grow your business and achieve unmatched results. Whether it’s common eCommerce security threats or a lack of digital marketing— we’ll work with you to overcome whatever challenges your business faces. Contact us for help with your eCommerce site.




